In my last previous post I have write about how to memory scanning using Cheat Engine, in thist post i will show you how to Read and Write process memory using C++ Function.
Read before start reading this article: This tutorial is for educational purposes only. the author(s) has no intention to use the knowledge for any undoings, please make sure that you are not violating the EULA/TOS of the specific game/application.
Getting started
So what kind function is that?
ReadProcessMemory Function
ReadProcessMemory copies the data in the specified address range from the address space of the specified process into the specified buffer of the current process. Any process that has a handle with PROCESS_VM_READ access can call the function.
Source : Docs Microsoft
WriteProcessMemory Function
WriteProcessMemory copies the data from the specified buffer in the current process to the address range of the specified process. Any process that has a handle with PROCESS_VM_WRITE and PROCESS_VM_OPERATION access to the process to be written to can call the function. Typically but not always, the process with address space that is being written to is being debugged.
The entire area to be written to must be accessible, and if it is not accessible, the function fails.
Source : Docs Microsoft
How to do
Lets say you want to Read and Write process memory without Cheat Engine. or want to Program a BOT in C++ Language, you can use this Function to achieve that. Lets start. in this tutorial I will show you how to make simple console application using that both Function here this we need to prepare:
- Visual Studio, I use this for C++ IDE
- Pointer to Address, I use this to Read and Write the value
- Some Basic Programming
For Visual Studio, you can download that in Microsoft site, I use the community version. For tutorial how to search a pointer for an Address you can see my tutorial in my previous post or click here => Game Hacking - Using Cheat Engine to-do Memory Scanning
Alright lets go..
GetModuleBase Function
Please use this Function in both Read and Write process memory code, this function used for Get base address from Process we want to target
DWORD GetModuleBase(const wchar_t* ModuleName, DWORD ProcessId) {
// This structure contains lots of goodies about a module
MODULEENTRY32 ModuleEntry = { 0 };
// Grab a snapshot of all the modules in the specified process
HANDLE SnapShot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPMODULE, ProcessId);
if (!SnapShot)
return NULL;
// You have to initialize the size, otherwise it will not work
ModuleEntry.dwSize = sizeof(ModuleEntry);
// Get the first module in the process
if (!Module32First(SnapShot, &ModuleEntry))
return NULL;
do {
// Check if the module name matches the one we're looking for
if (!wcscmp(ModuleEntry.szModule, ModuleName)) {
// If it does, close the snapshot handle and return the base address
CloseHandle(SnapShot);
return (DWORD)ModuleEntry.modBaseAddr;
}
// Grab the next module in the snapshot
} while (Module32Next(SnapShot, &ModuleEntry));
// We couldn't find the specified module, so return NULL
CloseHandle(SnapShot);
return NULL;
}
ReadProcessMemory
From previous tutorial, we got this pointer for seeing how many monster detected in the radar. the pointer is “RF_Online.bin” + 1F3B6E0 with Offset 170 First lets Include some important source file
Include source file
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <TlHelp32.h>
using namespace std;
DWORD pid;
int target;
Include GetModulBase Function
Add the Function GetModuleBase so our code look like this
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <TlHelp32.h>
using namespace std;
DWORD pid;
int target;
DWORD GetModuleBase(const wchar_t* ModuleName, DWORD ProcessId) {
// This structure contains lots of goodies about a module
MODULEENTRY32 ModuleEntry = { 0 };
// Grab a snapshot of all the modules in the specified process
HANDLE SnapShot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPMODULE, ProcessId);
if (!SnapShot)
return NULL;
// You have to initialize the size, otherwise it will not work
ModuleEntry.dwSize = sizeof(ModuleEntry);
// Get the first module in the process
if (!Module32First(SnapShot, &ModuleEntry))
return NULL;
do {
// Check if the module name matches the one we're looking for
if (!wcscmp(ModuleEntry.szModule, ModuleName)) {
// If it does, close the snapshot handle and return the base address
CloseHandle(SnapShot);
return (DWORD)ModuleEntry.modBaseAddr;
}
// Grab the next module in the snapshot
} while (Module32Next(SnapShot, &ModuleEntry));
// We couldn't find the specified module, so return NULL
CloseHandle(SnapShot);
return NULL;
}
Add main function
Then lets add the main() function
int main()
{
HWND hWnd = FindWindowA(0, ("RF Online")); // Change RF Online to your Windows name program you want to target
GetWindowThreadProcessId(hWnd, &pid); // This line used for get the ProcessID
HANDLE pHandle = OpenProcess(PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid); // We use this to get a Object handle for our passing parameter in ReadProcessMemory function
DWORD rf_client = GetModuleBase(L"RF_Online.bin", pid); // We find the base Address for RF_Online.bin process
DWORD baseAddress = rf_client + 0x1F3B6E0; // now we calculate our base address so it can form like this "RF_Online.bin" + 1F3B6E0
DWORD address = 0; // we initialize a address variable for our final address later
ReadProcessMemory(pHandle, (void*)baseAddress, &address, sizeof(address), 0); // we read the process memory address and save it to address variable we initialize before
address += 0x170; // we add our offset to this final address so now this address variable value is pointer to read detected monster in radar "RF_Online.bin" + 1F3B6E0 with Offset 170
// in this block we do loop for every 100ms to show update how much monster exist in our radar.
while (true) {
ReadProcessMemory(pHandle, (LPVOID)address, &target, sizeof(target), 0);
cout << target << endl;
Sleep(100);
system("CLS");
}
system("Pause");
}
Final Code
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <TlHelp32.h>
using namespace std;
DWORD pid;
int target;
DWORD GetModuleBase(const wchar_t* ModuleName, DWORD ProcessId) {
// This structure contains lots of goodies about a module
MODULEENTRY32 ModuleEntry = { 0 };
// Grab a snapshot of all the modules in the specified process
HANDLE SnapShot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPMODULE, ProcessId);
if (!SnapShot)
return NULL;
// You have to initialize the size, otherwise it will not work
ModuleEntry.dwSize = sizeof(ModuleEntry);
// Get the first module in the process
if (!Module32First(SnapShot, &ModuleEntry))
return NULL;
do {
// Check if the module name matches the one we're looking for
if (!wcscmp(ModuleEntry.szModule, ModuleName)) {
// If it does, close the snapshot handle and return the base address
CloseHandle(SnapShot);
return (DWORD)ModuleEntry.modBaseAddr;
}
// Grab the next module in the snapshot
} while (Module32Next(SnapShot, &ModuleEntry));
// We couldn't find the specified module, so return NULL
CloseHandle(SnapShot);
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
HWND hWnd = FindWindowA(0, ("RF Online")); // Change RF Online to your Windows name program you want to target
GetWindowThreadProcessId(hWnd, &pid); // This line used for get the ProcessID
HANDLE pHandle = OpenProcess(PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid); // We use this to get a Object handle for our passing parameter in ReadProcessMemory function
DWORD rf_client = GetModuleBase(L"RF_Online.bin", pid); // We find the base Address for RF_Online.bin process
DWORD baseAddress = rf_client + 0x1F3B6E0; // now we calculate our base address so it can form like this "RF_Online.bin" + 1F3B6E0
DWORD address = 0; // we initialize a address variable for our final address later
ReadProcessMemory(pHandle, (void*)baseAddress, &address, sizeof(address), 0); // we read the process memory address and save it to address variable we initialize before
address += 0x170; // we add our offset to this final address so now this address variable value is pointer to read detected monster in radar "RF_Online.bin" + 1F3B6E0 with Offset 170
// in this block we do loop for every 100ms to show update how much monster exist in our radar.
while (true) {
ReadProcessMemory(pHandle, (LPVOID)address, &target, sizeof(target), 0);
cout << target << endl;
Sleep(100);
system("CLS");
}
system("Pause");
}
And then now build our progream by pressing Ctrl + B, then open the console using Run As Admin. and then lets check our console program. it will update every 100ms to show value from address we add before,
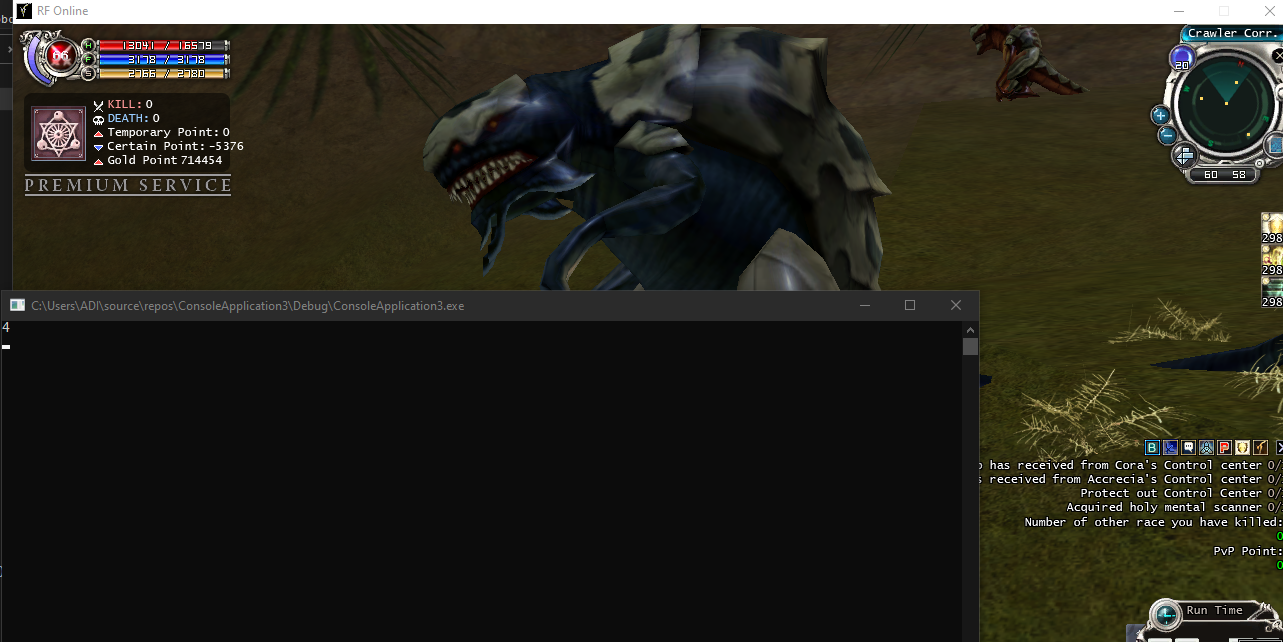
Console app show 4, same as the monster show in Radar
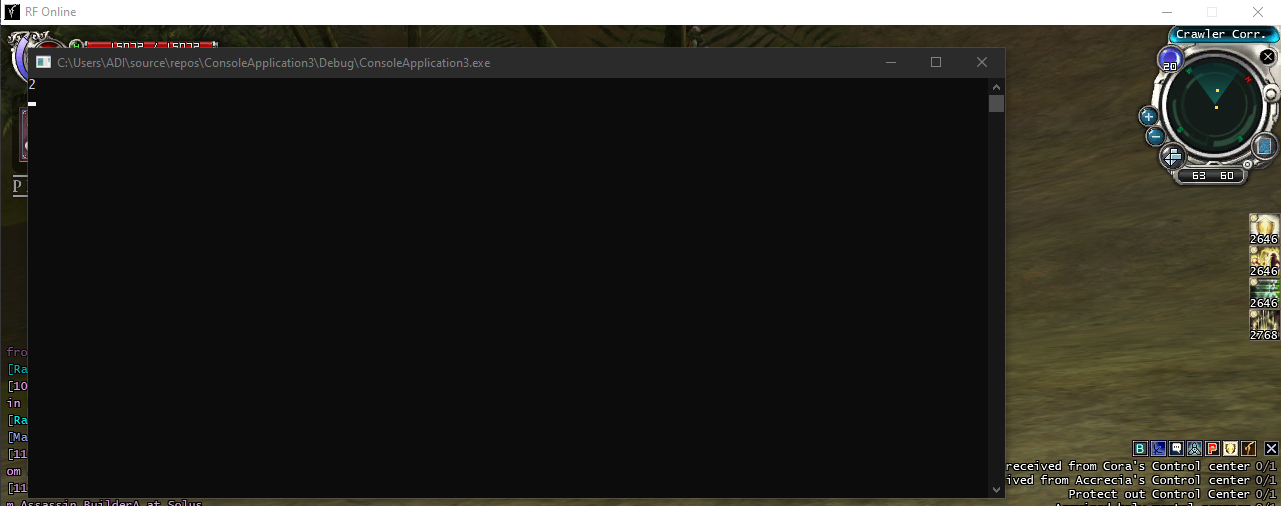
Console app update to 2, because i move my character. so the Radar also change
here the video for another example, this ReadProcessMemory from my character current target
WriteProcessMemory
The code is still same as ReadProcessMemory. the difference is just the pointer to the Address, in this tutorial I will use pointer for current target that i got before in my previous post
“RF_Online.bin” + B41214 with Offset 4
Full code
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <TlHelp32.h>
using namespace std;
DWORD pid;
int target;
DWORD GetModuleBase(const wchar_t* ModuleName, DWORD ProcessId) {
// This structure contains lots of goodies about a module
MODULEENTRY32 ModuleEntry = { 0 };
// Grab a snapshot of all the modules in the specified process
HANDLE SnapShot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPMODULE, ProcessId);
if (!SnapShot)
return NULL;
// You have to initialize the size, otherwise it will not work
ModuleEntry.dwSize = sizeof(ModuleEntry);
// Get the first module in the process
if (!Module32First(SnapShot, &ModuleEntry))
return NULL;
do {
// Check if the module name matches the one we're looking for
if (!wcscmp(ModuleEntry.szModule, ModuleName)) {
// If it does, close the snapshot handle and return the base address
CloseHandle(SnapShot);
return (DWORD)ModuleEntry.modBaseAddr;
}
// Grab the next module in the snapshot
} while (Module32Next(SnapShot, &ModuleEntry));
// We couldn't find the specified module, so return NULL
CloseHandle(SnapShot);
return NULL;
}
int main() {
HWND hWnd = FindWindowA(0, ("RF Online"));
GetWindowThreadProcessId(hWnd, &pid);
HANDLE pHandle = OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, pid);
DWORD rf_client = GetModuleBase(L"RF_Online.bin", pid);
DWORD baseAddress = rf_client + 0xB41214;
DWORD address = 0;
ReadProcessMemory(pHandle, (void*)baseAddress, &address, sizeof(address), 0);
address += 0x4;
while (true) {
DWORD i;
cout << "Input monster code in 4-byte data: ";
cin >> i;
ReadProcessMemory(pHandle, (LPVOID)address, &target, sizeof(target), 0);
cout << "Monster code BEFORE writing proc memory : " << target << endl;
cout << "\n" << endl;
WriteProcessMemory(pHandle, (void*)address, &i, sizeof(i), nullptr);
cout << "Start writing the proc memory\n" << endl;
ReadProcessMemory(pHandle, (LPVOID)address, &target, sizeof(target), 0);
cout << "Monster code AFTER writing proc memory : " << target << endl;
system("Pause");
system("CLS");
}
system("Pause");
}
Here the video how it work